That lump-in-the-throat feeling can show up out of nowhere—tight, persistent, and impossible to ignore. It…
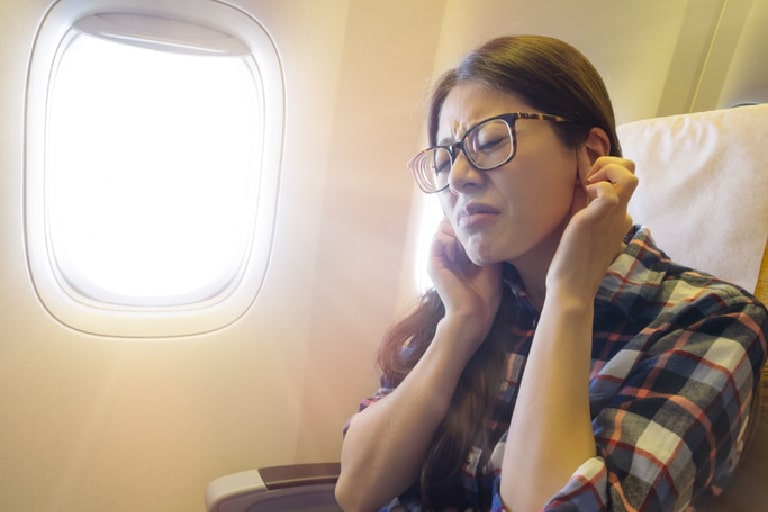

Expert Tips for Traveling with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Summer will be here soon, which means it’s time to start making vacation plans. While most people book flights and hotels without much worry, patients with Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) may be concerned about the effects of their condition if they plan on traveling on airline flights.
Flying can be challenging for those with ETD. The change in air pressure during takeoff and landing can damage the middle ear and, sometimes, the inner ear. Many people with ETD will experience discomfort, pain, and even temporary hearing loss when flying.
Fortunately, these challenges don’t mean you must stay grounded when traveling. You can make your next flight more manageable and enjoyable with some proactive measures and strategies. In this post, we’ll discuss Eustachian tube dysfunction and how to manage ETD while flying.
Understanding Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Before we delve into our tips on managing ETD while flying, let’s ensure we understand Eustachian tube dysfunction clearly.
What is a Eustachian Tube?
A Eustachian tube is a narrow passage that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and upper throat.
The Eustachian tubes serve a number of purposes, including:
- Draining fluid from the middle ear
- Balancing pressure in the middle ear
- Protecting the ear from nasal drainage
What is Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
The Eustachian tube has a valve that opens and closes. When this valve has trouble opening and closing, it can cause a buildup of fluid in the ears or pain and pressure in the ear. Some people also feel persistent pressure and hear unusual sounds. ETDs are very common and are the main cause of ear infections. ETDs are usually caused by factors like allergies, sinus infections, colds, or anatomical issues.
Eustachian tube dysfunction includes the following varieties:
- Patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction: This type of ETD happens when Eustachian tube valves remain open, allowing sound to travel from the nasal-sinus cavity to the ears. People with this type of ETD will often loudly hear the sounds of their blood pumping or their breathing.
- Obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction: This variation of ETD happens when the Eustachian tube valve remains closed or does not open as it should, preventing fluids from draining out of the ear and pressure balance.
- Baro-Challenge-Induced Eustachian tube dysfunction: This type of ETD is what is felt when participating in activities like flying or scuba diving. The tube does not open as it should, causing ear pain and muffled hearing.
Some cases of ETD will resolve on their own or with at-home treatments. However, severe or recurring cases may require medical intervention, including pressure equalization tubes.
Tips for Managing Eustachian Tube Dysfunction While Flying
During ascension and descension of the plane, the Eustachian tube should allow pressure to escape, allowing the pressure of the middle ear to balance with the cabin air pressure.
Many people experience pressure in their middle ear when flying, especially during landing. This pressure is due to the Eustachian tube becoming locked in a closed position. In this case, most find relief and can open the tube with the following techniques during takeoff and landing:
- Yawning
- Swallowing
- Chewing gum
- Hold your nostrils closed and your mouth shut, and gently blow out air (also called “popping” your ears or the Valsalva maneuver)
Unfortunately, people with Eustachian tube dysfunction will often have trouble equalizing the pressure in their middle ear when flying and experience more severe symptoms. In addition to the strategies listed above, here are some tips for those who experience more severe ETD issues.
- Stay Hydrated: Of course, everyone should be sure to stay hydrated, but when flying, drinking plenty of water can help keep the mucous membranes in the nose and throat moist, facilitating better functioning in the Eustachian tube.
- Nasal Decongestants: Using nasal decongestants about 30 minutes before takeoff and landing can help reduce nasal congestion and improve Eustachian tube opening.
- Specialized Earplugs: A few brands of specialized earplugs are on the market. They help regulate air pressure changes and alleviate discomfort associated with ETD.
If you frequently experience ETD or have severe symptoms, consult with an ENT specialist before your flight. They will be able to recommend specific medications and treatments to alleviate your symptoms.
Learn More About Managing Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction can make air travel uncomfortable, but with the right strategies, you can mitigate the effects and enjoy a smooth flight and a pleasant summer vacation. Remember to stay hydrated, use nasal decongestants as needed, and practice techniques like chewing gum or the Valsalva maneuver to equalize ear pressure.
At ExcelENT of Alabama, our experienced specialists dedicate themselves to providing effective diagnosis and personalized treatment options for ETD. We use advanced techniques to alleviate symptoms and restore proper Eustachian tube function.
If you are struggling with managing Eustachian tube dysfunction symptoms, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment to experience the quality care we provide to our ear, nose, and throat patients in Birmingham, AL.
Get Help with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction at Excel ENT
If you are experiencing severe or recurring symptoms of ETD, don’t put off making an appointment at Excel ENT. Our team will work diligently to diagnose your issue and tailor a treatment plan using cutting-edge technology and techniques.
Schedule an appointment online, or call to discuss coming in at a time that’s best for you: 205-651-8764.